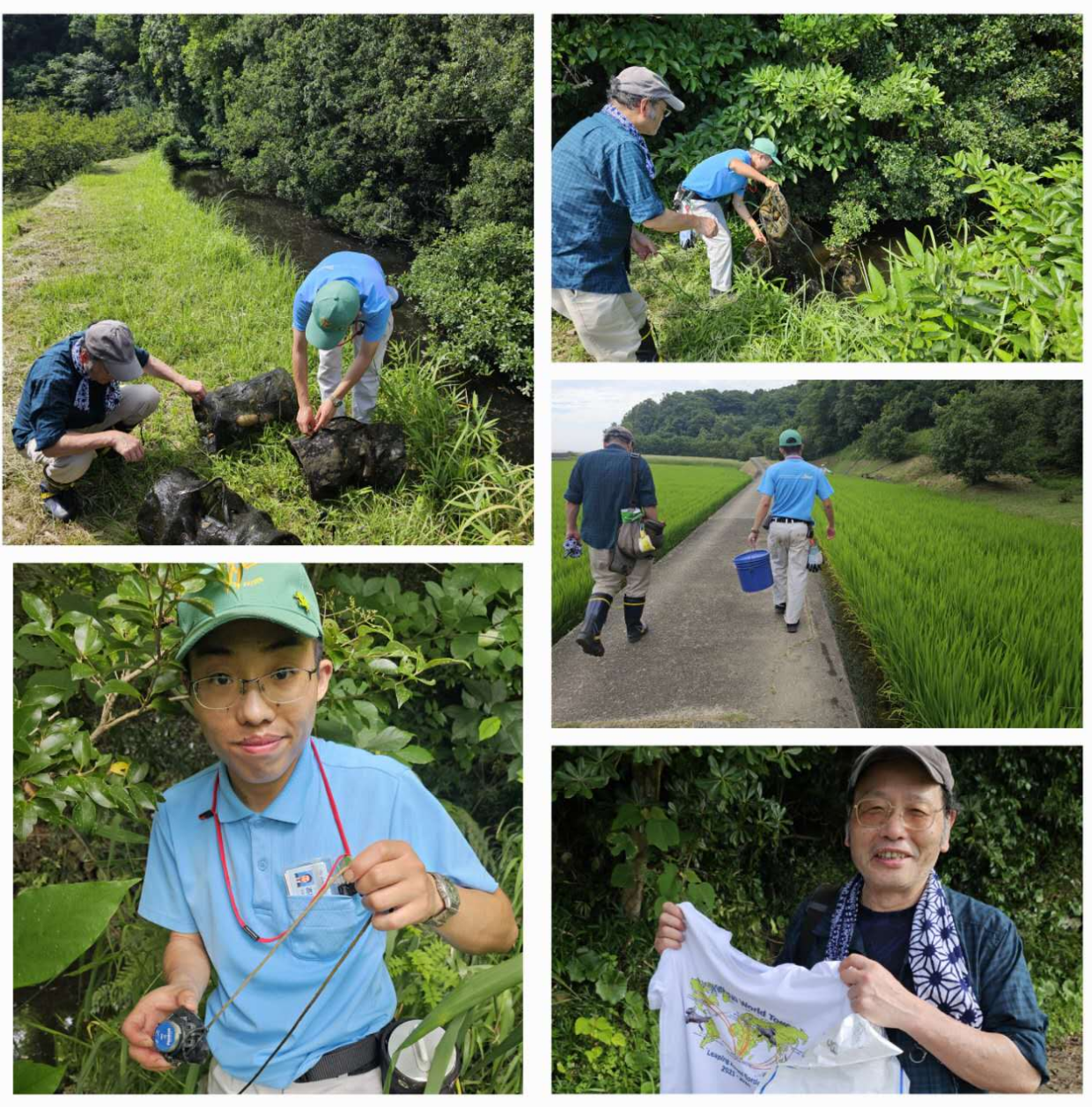
A joint meeting of the Herpetological Association of Africa and the African Amphibian Working Group in Wilderness, South Africa: 26 – 29 November 2024
Each of these groups usually meets every two years separately, so it was for the first time in their existance that they met in back-to-back meetings in Wilderness South Africa. First up was the 20th meeting of the AAWG, with plenty of familiar faces from across the globe.

Next was the 16th meeting of the HAA, which also had great representation and considerably more delegates.

The meeting featured presenters from 9 different African countries: Madagascar, Nigeria, Tanzania, Uganda, Ethiopia, Kenya, Ghana, Namibia and South Africa. This was certainly the best representation of the continent since each of the meetings started.
The following talks featured MeaseyLab members:
Home and away: the gut microbiome of Xenopus laevis in native and invasive populations
John Measey; Jiankun Yu; Dareen Almojil; Stephane Boissinot; Laurie Araspin; Carla Wagener; Greg Pauly; Reed Ojala-Barbour; Claudio Soto-Azat
The vertebrate gut microbiome is a community largely composed of bacterial, fungal and viral components, whose molecular component equal that of the host. The influence of the microbiome is known to be significant both on an individual basis, and also on population scales in a wide range of host organisms. The gut microbiome is known to be involved with key attributes of animal health, including assimilation of nutrients, immuno-defensive functions and host behaviour. In this study, we used bacterial 16S rRNA amplicon-based sequencing for metataxonomic classification of the gut microbiome of individuals from 12 native populations of Xenopus laevis. These populations were selected to represent the native range of the host species. From the 16S rRNA community profiles, we determine the components of the core microbiome of X. laevis and ask whether deviations from the core are associated with the environmental context in which they live. In addition, we sampled populations from Chile (4) and USA (7) to determine what aspects of the core microbiome are retained by non-native populations. This represents the first time that the microbiome of X. laevis has been assessed across such diverse conditions and provides data that will help understand the role played by the environment within this model organism.
Southern Africa Amphibian Red List Project – updated assessments for the region lead the GAA3
Jeanne Tarrant; Joshua Weeber; Oliver Angus; Adrian J. Armstrong; Ninda L. Baptista; Francois S. Becker; Rebecca M. Brunner; Werner Conradie; Louis H. du Preez; James Harvey; Adriaan Jordaan; Keir Lynch; John Measey; Mohlamatsane Mokhatla; Darren W. Pietersen; Fortunate M. Phaka; Jennifer Swanby; Krystal A. Tolley; Andrew A. Turner; Luke Verburgt
As the most threatened vertebrate class on earth, amphibians are leading the biodiversity extinction crisis. The 2nd Global Amphibian Assessment (GAA2) found that 41.5% of species globally are at risk of extinction, these extraordinary and diverse creatures are experiencing the worst population declines and highest extinction risk of any vertebrate group. South Africa has a good history of updating Red List assessments and has done so consistently since 2004 with the publication of the Atlas and Red Data Book. As some of the first assessments to contribute to GAA3, regional updates are in process for 246 southern African amphibian species. A very high proportion (approximately 74%) are endemic to the region, emphasizing the need to understand their conservation status, and prioritize conservation resources. Over 150,000 records were collated from 16 institutions (including citizen science platforms) and numerous private collections. A team of twenty experts contributed to assessment updates, with the support of the IUCN Amphibian Red List Authority, Amphibian Arc, SANBI and Re:Wild. Applying the IUCN Red List criteria according to IUCN guidelines, the current assessments have resulted in category changes for over 40% of priority species, including assigning a status to all but one Data Deficient species and all Not Evaluated species. Future climate scenarios (2050s) were modelled for South Africa’s threatened frog species and predict a wide range of distributional impacts, which will be exacerbated by ongoing land-use change. 35% of threatened species are likely to be highly impacted by future climate change scenarios. The updated assessments will be published by IUCN in the first half of 2025, and the outcomes of this work will be invaluable in informing an updated conservation and research strategy, the National Biodiversity Assessment, and has already contributed to identifying species in need of urgent recovery in the next decade.
The BioSoundSCape project: Automating frog detection for ecological monitoring in the Cape Floristic Region
Andrew A. Turner; John Measey; Oliver Angus; Colleen Seymour; Alan Lee; Rose Snyder; Festus Adebgola; Leo Salas; Matt Clarke
Monitoring frogs has the potential to provide useful insights into measuring ecosystem health and the management of these ecosystems. Yet currently this monitoring is highly restricted, in space and time consuming. Data acquired from automated sound recording devices can extend the reach of ecological monitoring. The BioSCape project is a large, multi-party collaboration with NASA that aims to relate biodiversity patterns on the ground with remotely sensed, cutting edge spectral imaging that provides very high spectral resolution across the electromagnetic spectrum. One of the novel ways to measure biodiversity is to measure bioacoustic diversity. The BioSoundSCape project deployed a large number of automated sound recorders (AudioMoths) across the Cape Floristic Region and recorded nearly 1 million sound recordings. These recordings are freely available on NASA’s Distributed Active Archive Center. The project set up pattern matching algorithms to detect frog calls of 13 frog species, ran statistical pattern matching, validated results and used the resultant validated sound sonographic signatures for training input to a machine learning (computational neural network) system as implemented by RFCx in Arbimon. From this we calculated diversity indices and present examples of these outputs. Once the entire data collection, processing and analysis can be automated, it can realise the ability for large-scale, frog and ecosystem monitoring.